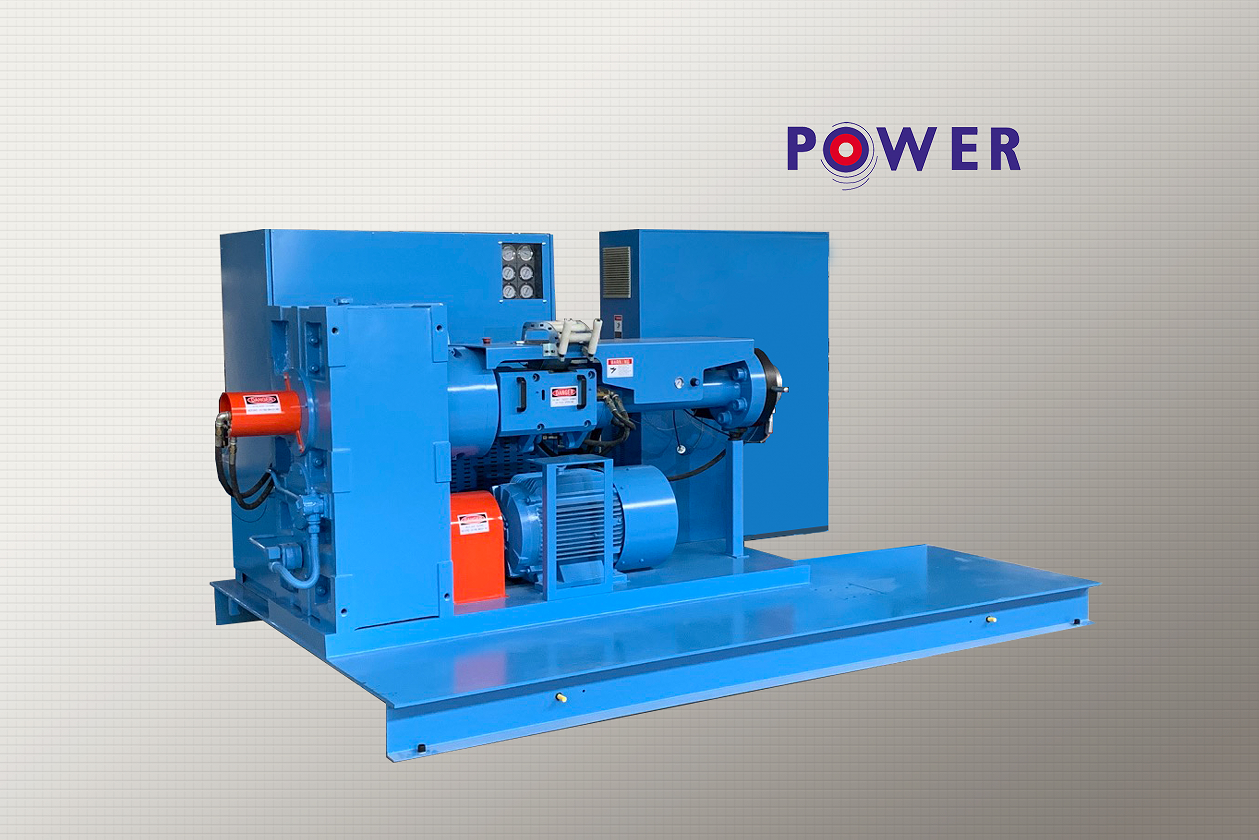
The rubber extruder stands as a cornerstone of polymer processing, a versatile and robust machine essential for shaping rubber compounds into a myriad of continuous profiles. Its operation, based on the principle of forcing viscoelastic rubber material through a die of specific shape, is deceptively simple. Yet, the engineering behind it and its resulting characteristics make it indispensable across industries, from automotive to construction.
Key Characteristics of Rubber Extruders
Modern rubber extruders, primarily of the screw-type design, exhibit several defining characteristics that enable their widespread use:
1. Continuous and Efficient Processing: Unlike batch processes, extruders operate continuously,rubber extrusion equipment, receiving rubber compound (usually in strip form from a mixer) and outputting a constant, uniform profile. This ensures high production rates, consistent product quality, and efficient material use with minimal waste.
2. Versatility in Output: By simply changing the die head, a single extruder can produce an enormous variety of cross-sectional shapes—solid, hollow, or complex multi-component profiles. This includes simple seals, intricate automotive trim, tire treads, and tubing of various diameters.
3. Intensive Mixing and Homogenization: The screw design, often with mixing sections or pins, provides significant shear and compressive forces. This action thoroughly homogenizes the rubber compound, dispersing additives like carbon black uniformly and ensuring consistent viscosity and properties throughout the extrudate.
4. Thermal Control and Vulcanization Prep: The extrusion barrel is divided into multiple temperature-controlled zones. This allows precise management of the rubber’s temperature profile, plastifying the material optimally for extrusion. Modern extruders often integrate with hot-air or microwave curing lines, preparing the profile for immediate vulcanization.
5. Adaptability to Material Variations: Extruders can process a wide range of rubber compounds, from natural rubber (NR) and styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) to more specialized polymers like ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) and silicone. Adjustments in screw speed, temperature, and die design accommodate different material flow properties (rheology).
6. Integration with Downstream Equipment: A key strength is its ability to function as the heart of a production line. It seamlessly integrates with roller die systems for tire treads, crossheads for wire and cable coating, cutters, cooling tanks, and continuous vulcanization systems, enabling fully automated production.
Primary Applications in Industry
The unique characteristics of rubber extruders translate into critical applications across numerous sectors:
· Tire Manufacturing: This is one of the most significant applications. Specialized tread extruders, often with roller dies, produce the precise tread patterns and sidewall profiles. Other extruders are used for inner liners, apex strips, and various rubber components within a tire. rubber extruder machine manufacturers in china,The ability to co-extrude different rubber compounds is crucial here.
· Automotive Components: The automotive industry relies heavily on extruded rubber profiles for sealing systems (door seals, window seals, trunk seals), hoses (coolant, air intake), dust boots, and trim. EPDM is exceptionally common here due to its weather resistance.
· Wire and Cable Insulation and Sheathing: Using a crosshead die, extruders precisely coat copper or aluminum wires with insulating layers (e.g., from EPR, XLPE) and outer protective jackets (often from PVC or halogen-free rubber compounds). This application demands extreme precision in concentricity and thickness.
· General Rubber Goods: This broad category includes hydraulic and pneumatic hoses, various tubes for medical or industrial use, rubber strips for machinery seals, refrigerator gaskets, and solid or sponge weather-stripping for buildings.
· Construction and Infrastructure: Extruded rubber is used in expansion joints for bridges and buildings, silicone roller covering strips for textile machinery,waterproofing membranes, gaskets for glazing, and profiles for roofing systems.
· Consumer Goods: Applications range from household appliance gaskets and tool grips to sports equipment and shoe soles.
In conclusion, the rubber extruder is a paradigm of efficient, continuous manufacturing. Its characteristics of versatility, continuous output, and precise process control solve fundamental production challenges for shaping rubber. As material science advances and demand for complex, high-performance rubber products grows, the extruder continues to evolve—incorporating smarter process control, advanced screw designs, and better integration with downstream systems. It remains, unequivocally, a vital machine in translating raw rubber compounds into the essential components that modern life and industry depend upon.
Post time: Feb-05-2026